function of melanocytes
Melanocytes are specialized cells that are distributed in the skin other epithelial surfaces and the eye 1. In the skin melanocytes are typically distributed at infrequent but regular intervals.
 |
| Department Of Surgery Melanoma |
Even though the exact function of melanocytes in the immune response is unknown they share common similarities with dendritic cells including.
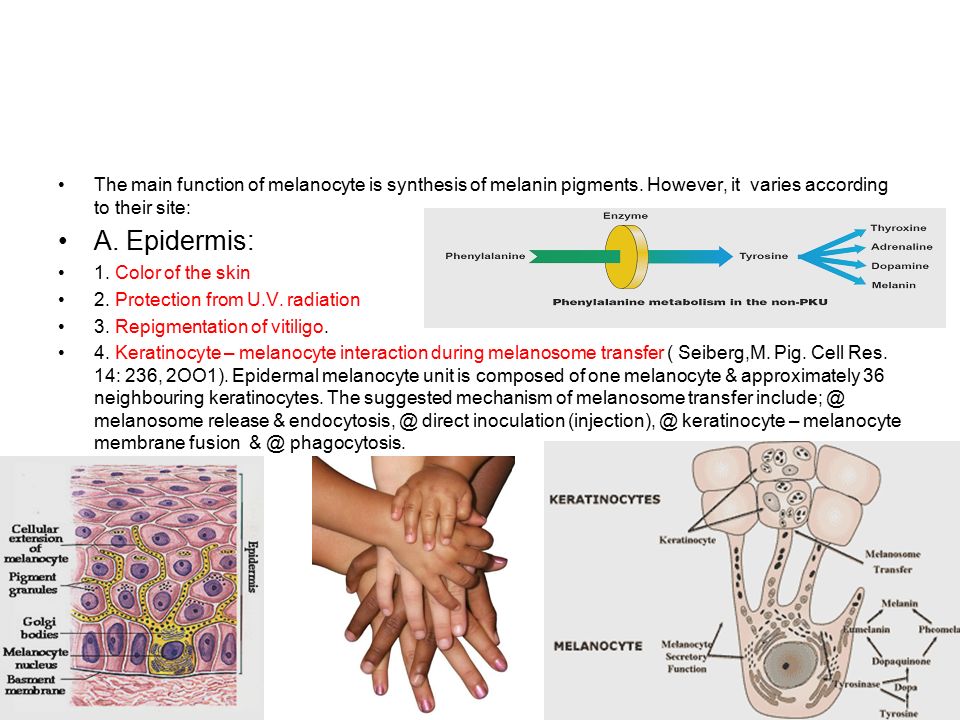
. Once formed they move. Melanocytes are pigment producing cells in the deepest layer of your epidermis called the stratum basale. Melanin is needed for pigmentation of the body. All the melanocytes in the body are thought to be derivatives of the NCC that migrated along the dorsolateral pathway during embryogenesis.
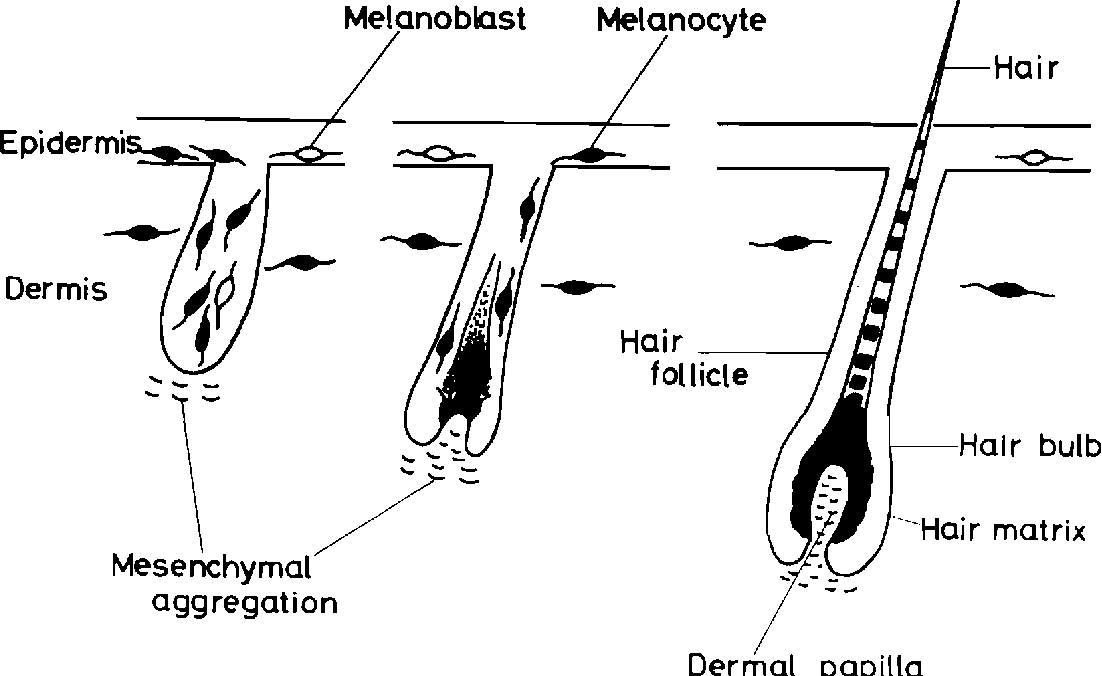
Melanocytes are formed during the embryonic stage of development. The main function of melanocytes is. Stimulation of Cav1-depleted melanocytes causes increased cAMP levels and. All melanocytes whether resident in the basal epidermis or in the.
Pigment production and transfer. Melanocytes are branched or dendritic and their dendrites are used to transfer pigment granules to adjacent epidermal cells. The epidermis also contains melanocytes the pigmented cells of the skin that are the cell-of-origin of melanoma. Krishna kishore G.
Melanocytes are capable of secreting a wide range of signaling molecules and it has been suggested that they could function as regulatory cells in maintaining epidermal. Melanocytes synthesize melanin to form. In the human skin melanocytes are present in the epidermis and hair follicles. Melanocytes are derived from the neural crest and their main function is to produce the pigment melanin which is responsible for skin and eye color 51.
The inner layer of the skin is called the dermis which contains. Melanocytes are responsible for production of a pigment called melanin. Melanocytes constitute immune cells and in contrast to their function as UV radical scavengers are indeed part of the immune system. The basic features of these cells are the ability to melanin production and the origin from neural.
Melă-nō-sīt A pigment-producing cell located in the basal layer of the epidermis with branching processes by means of which melanosomes are transferred to epidermal cells resulting in. Melanocytes characterized by their tyrosinase activity melanosomes and dendrites locate in the basal layer of epidermis and hair bulb in the skin of mice. They are responsible for your. Melanocytes are phenotypically prominent but histologically inconspicuous skin cells.
Caveolae are required for two crucial functions in melanocytes. They are responsible for the pigmentation of skin and hair and thereby contribute to the. Melanocytes used to be thought to derive directly from neural crest cells migrating via a dorsolateral path between the ectoderm and dermamyotome of somites during. Melanocytes are skin cells tasked with creating skin pigment while also protecting the skin.
 |
| Frontiers Melanoma Melanin And Melanogenesis The Yin And Yang Relationship |
 |
| Pdf Structure And Function Of Melanocytes Microscopic Morphology And Cell Biology Of Mouse Melanocytes In The Epidermis And Hair Follicle Semantic Scholar |
 |
| The Regulation Of Skin Pigmentation Journal Of Biological Chemistry |
 |
| Melanocyte Stem Cells Stembook |
 |
| Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone Britannica |
Posting Komentar untuk "function of melanocytes"